What is a Bolt?
A bolt is a form of threaded fastener with an external male thread requiring a matching pre-formed female thread such as a nut. Bolts are very closely related to screws.
A bolt is a type of mechanical fastener that consists of a shaft with threads and is used to hold two or more parts together. The shaft of the bolt is inserted through aligned holes in the parts that need to be fastened, and a nut is then screwed onto the threads of the bolt to provide clamping force and prevent axial movement.
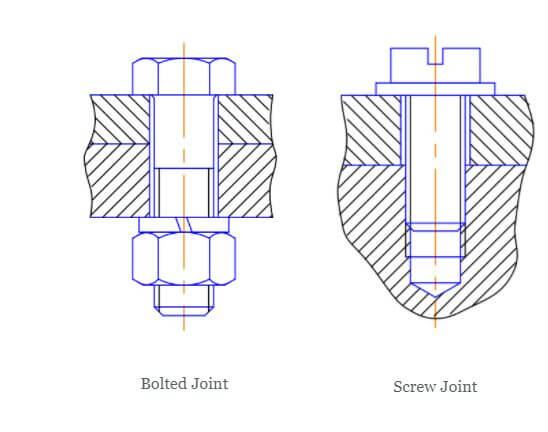
According to some definitions, whether a fastener is a bolt or a screw depends on how it is used. A bolt is inserted through unthreaded holes in the parts being fastened, while a screw may pass through a hole with threads that mate with threads in one of the parts.
In practice, however, the distinction between bolts and screws is not always clear, and the term “bolt” is often used to refer to any fastener with a threaded shaft.
Bolts are designed to prevent both radial and axial movement of the parts they are fastening. The unthreaded shank of the bolt provides an interface with the parts that are more precise and less abrasive than the threaded portion.
The shank also does not contain stress concentrations that could lead to failure, so it is important that it extends well beyond the interface between parts if a significant shear force will be placed on the bolt.
When a bolt is tightened, torque is applied to the head to generate axial force. This force acts between the bolt head and whatever the bolt is screwed into, whether that is a nut or one of the parts being fastened.
This causes elongation of the bolt and compression of the parts containing clearance holes. Alternatively, a locking nut or thread-locking adhesive can be used to prevent the bolt from loosening.
Parts of Bolt
These are different parts of the bolt described as follows.
- Head: The head is the top part of a bolt. It serves as a gripping surface for tools. To tighten or loosen a bolt, a tool with the appropriate bit must grip the head. Most bolts have a wrench-type head.
- Shank: The shank is located under the head. The shank is the smooth part of an unthreaded bolt. It should prevent radial movements of the joined workpieces. Without a shank, there is a greater chance that the bolt will loosen. Some workpieces generate vibrations, others are exposed to vibrations in their environment.
- Grip length: It is the part of the bolt that accommodates the parts which are to assemble. The grip length should be equal to the combined thickness of the joining parts.
- Threading: All bolts are threaded. Threading is what allows a bolt can be driven into or out of workpieces. Most bolts, however, are not entirely made up of threads. They have a head followed by a smooth shank and finally the threading.
- Thread length: It is the part of the bolt that accommodates the nut.
- Nominal length: It is the sum of thread length and grip length (as shown in the figure).
Difference between Bolts and Screws
A bolt is a non-tapered fastener that uses a washer and nut to hold objects together. A screw is a tapered fastener that mates with an existing thread or creates its own thread in material as it turns.
Type of bolt heads
Bolts, as well as screws, are available in a vast variety of head shapes. These heads are made in order to grip the tools that are used to tighten them.
The most common type of bolt head types includes square, hex, slotted hex washer, and socket cap.
The earliest bolt heads in use were the square heads. Square heads consist of a square indentation on the head followed by a shaft that withstands rotation when a torque is applied to it. Square heads are still in use today but hex heads have become more common. Hexagonal heads are used with a wrench or a spanner to provide torque.
There are numerous other head shapes in use as well, namely:
- Flat bolt head: A counter shank head with a flat top.
- Oval bolt head: A counter shank head with a rounded head top.
- Pan bolt head: A slightly rounded head with a short vertical side.
- Truss bolt head: An extra-wide head with a rounded top.
- Round bolt head: A Dome’s head.
- Hex bolt head: A hexagonal head.
- Hex washer bolt head: A Hexagonal head with a round washer at the bottom.
- Slotted hex washer bolt head: A hexagonal head with a built-in washer and slot.
- Socket cap bolt head: A small cylindrical head using a socket driver.
- Button bolt head: A low-profile rounded head with a socket driver.
However, there are many similarities between bolts and screws, there are some differences too.
Machinery’s Handbook explains that a bolt is used to assemble unthreaded objects, usually using a nut. In comparison, screws are used to assemble objects with threads. The thing is though: not all items that use screws are already threaded.
What is a Bolt Used for?
Bolt uses the following conditions when:
- The parts that are fastened, require frequent dismantling and reassembly.
- When the parts that are fastened, are made of a material that is too weak to make durable threads.
- The parts that are fastened have medium thicknesses. For example, beams, flanges or plates, etc.
- When there is a place available for bolt head and nut.
- There is a place available for a spanner.
advantages and disadvantages of screws and bolts fastener
- Screws are cheaper compared to bolts.
- Bolts are good for frequent dismantling and reassembling, unlike screws.
- Bolts carry the load on a larger shank area when compared to the screw.






